What is a Valve?
Valves are integral components used in various industries, serving as control devices to regulate the flow of fluids or gases within a system. They play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and safety of many processes, from industrial applications to household plumbing. In this article, we will explore the world of valves, their types, how they work, their applications, materials, design considerations, maintenance, and future trends.
Types of Valves
Valves come in a variety of types, each designed to fulfill specific functions:
Gate Valves
Gate valves control flow by raising or lowering a gate. They are commonly used in the oil and gas industry.
Ball Valves
Ball valves utilize a spherical disc to control flow. They are often preferred in applications requiring on/off control.
Globe Valves
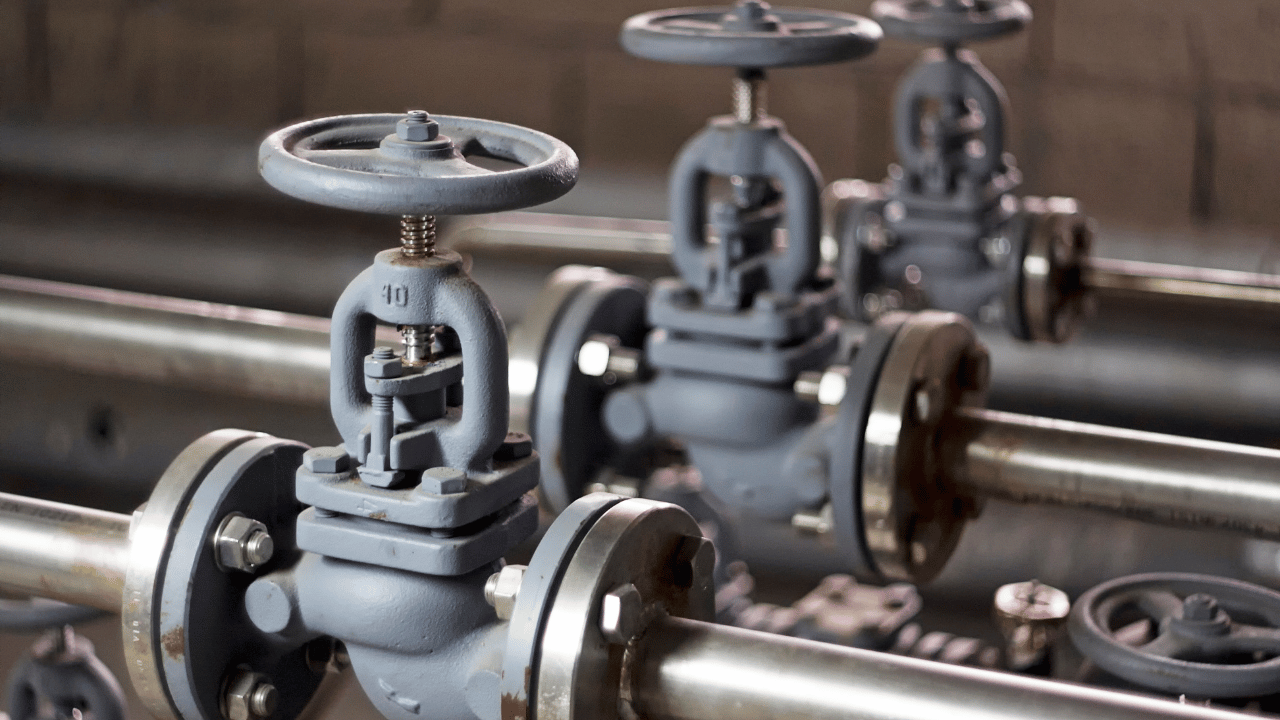
Globe valves regulate flow with a plug and seat mechanism. They offer precise control and are used in various industries.
Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves control flow using a circular disc mounted on a rotating shaft. They are widely used in water treatment plants.
How Do Valves Work?
Valves work on a fundamental principle where the flow of fluid or gas is regulated by opening or closing a passage. The mechanism depends on the type of valve, but the common objective is to control the flow and pressure within a system.
Common Applications of Valves
Valves find applications in various industries, including:
Oil and Gas Industry: Valves are vital in controlling the flow of crude oil and natural gas in pipelines.
Water Treatment Plants: They are used in water distribution systems for regulating the flow of potable water.
Household Applications: Valves are commonly found in plumbing systems, controlling water flow in our homes.
Valve Materials
Valve materials vary depending on the intended use:
Metals: Stainless steel, cast iron, and bronze are common metals used for their durability.
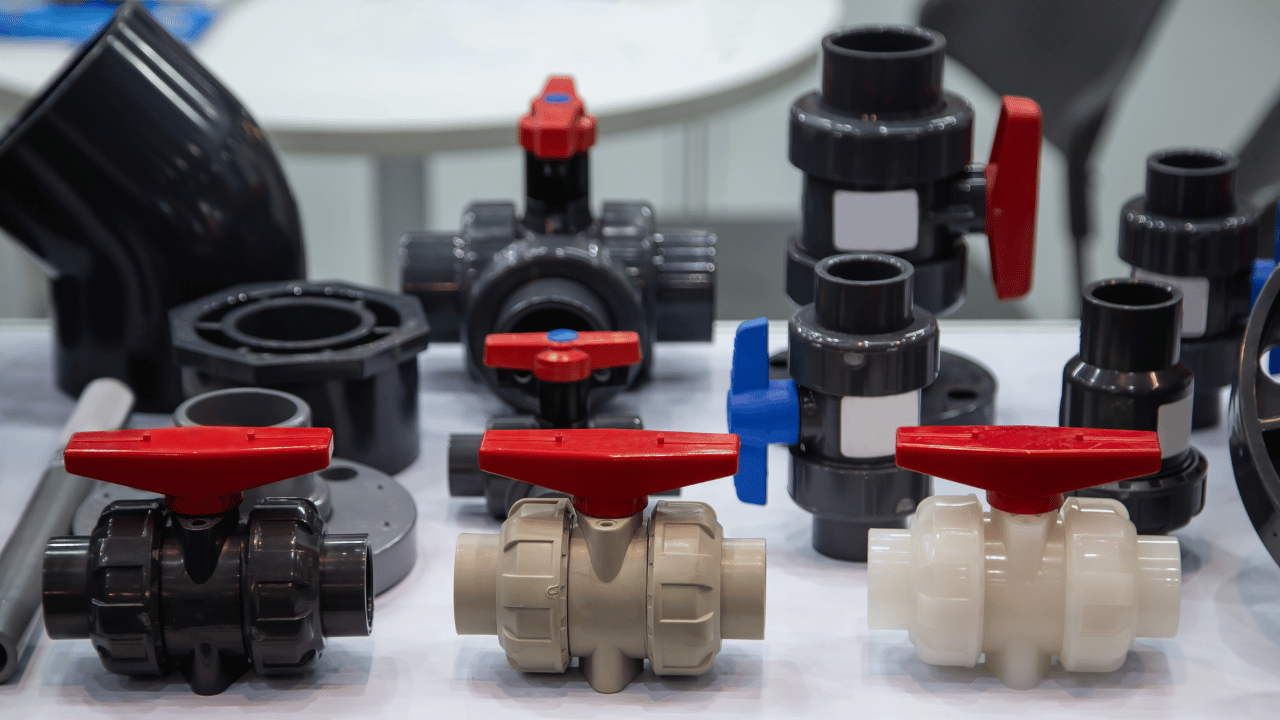
Plastics: PVC and CPVC are popular in applications where corrosion resistance is essential.
Composites: Fiber-reinforced composites offer a blend of strength and corrosion resistance.
Valve Design Considerations
When selecting valves, several factors must be considered:
Size and Pressure Rating: Valves must be appropriately sized to handle the flow, and their pressure rating should match the system’s requirements.
Temperature Compatibility: Valves should be able to withstand the temperature of the fluid or gas they are controlling.
Environmental Factors: In some cases, valves may need to resist corrosive environments or meet specific safety standards.
Valve Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the long-term functionality of valves. Neglecting maintenance can lead to leaks and system failures. To ensure a valve’s longevity:
- Inspect valves for wear and tear regularly.
- Lubricate moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Replace seals and gaskets as needed to prevent leaks.
Future Trends in Valve Technology
The world of valves is not immune to technological advancements. Two promising trends are emerging:
Smart Valves: These valves can be remotely monitored and controlled, improving efficiency and maintenance.
Environmentally Friendly Designs: Valves are being developed with sustainability in mind, aiming to reduce waste and emissions.
Conclusion
Valves are unsung heroes in many industries, ensuring the smooth flow of fluids and gases in various applications. Understanding the different types, how they work, their materials, and design considerations is essential to make informed decisions in selecting and maintaining them.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why are valves crucial in the oil and gas industry?
A1. Valves in the oil and gas industry help control the flow of crude oil and natural gas in pipelines, ensuring safe and efficient transportation.
Q2. What is the significance of temperature compatibility in valve selection?
A2. Temperature compatibility ensures that the valve can withstand the temperature of the fluid or gas it is controlling, preventing damage or failure.
Q3. How do smart valves enhance efficiency?
A3. Smart valves can be remotely monitored and controlled, reducing downtime, and improving maintenance, making processes more efficient.
Q4. Are there valves suitable for environmentally conscious applications?
A4. Yes, there are environmentally friendly valve designs that aim to reduce waste and emissions, promoting sustainability.
Q5. How can regular maintenance extend the lifespan of valves?
A5. Regular maintenance includes inspections, lubrication, and replacement of seals, ensuring valves function optimally and have a longer lifespan.








1 thought on “What is a Valve?”